The automotive industry is witnessing a significant shift in user interface design, moving towards hybrid interfaces that combine the best aspects of touch screens and physical controls. This evolution is driven by a growing recognition of the importance of automotive user experience, safety concerns, and the need for intuitive interactions in modern vehicles. Let us explore the evolution, importance, and trends of hybrid interfaces in the automotive world.
Evolution of Automotive Interfaces
The journey of automotive interfaces has been marked by several key phases:
Analog Era
In the early days of automobiles, interfaces were purely mechanical, consisting of basic controls like steering wheels, pedals, and levers. As technology advanced, cars began incorporating more electrical systems, leading to the introduction of buttons and knobs for various functions.
Digital Revolution
The late 20th and early 21st centuries saw a rapid digitization of car interfaces. Touch screens, first introduced in luxury vehicles, quickly became ubiquitous across various car segments. This shift was inspired by the success of smartphones and tablets, with automakers aiming to replicate the sleek, minimalist aesthetic of these devices.
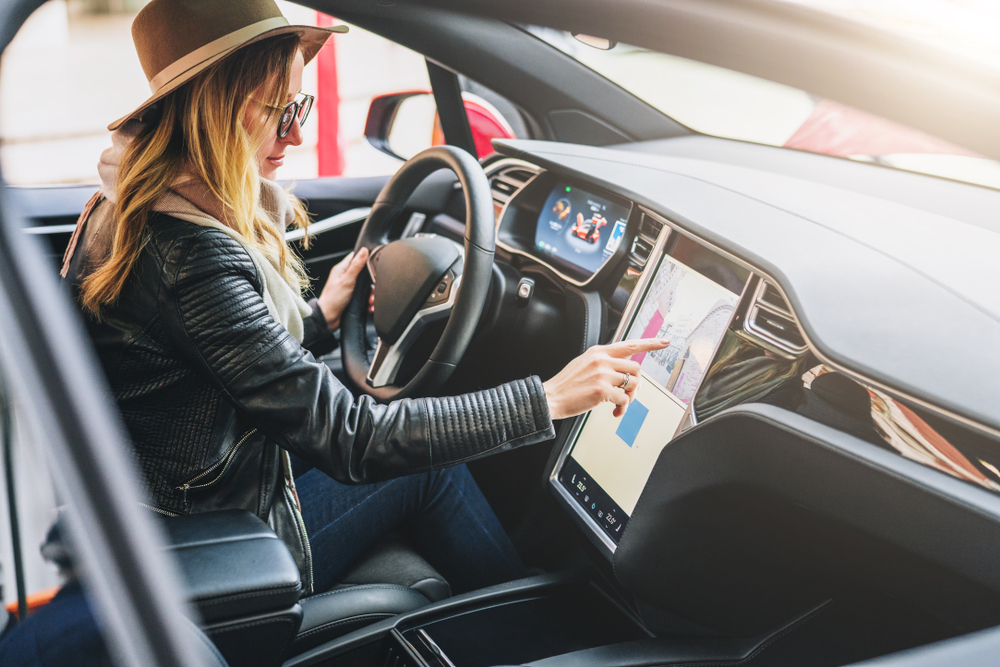
Touch Screen Dominance
Many automakers, following Tesla’s lead, embraced large touch screens as the primary interface for vehicle controls. This trend reached its peak with models like the Tesla Model 3, which consolidated almost all controls into a single, large touch screen.
Hybrid Approach
Recent years have seen a pendulum swing back towards a more balanced approach. Manufacturers are now recognizing the value of combining touch screens with physical controls, creating hybrid interfaces that offer both flexibility and tactile feedback.
The shift towards hybrid interfaces is driven by several key factors:
Safety Considerations
Touch screens can be distracting for drivers, potentially leading to dangerous situations. Studies have shown that tasks can take up to 40 seconds longer to complete on touch screens compared to physical control. This has prompted safety organizations to act, with the European New Car Assessment Program planning to require physical buttons for critical functions to achieve top safety ratings by 2026.
User Experience
Physical buttons offer immediate tactile feedback, confirming actions without requiring visual attention. This is particularly important for frequently used functions like climate control or volume adjustment. Hybrid interfaces allow for a more intuitive and less distracting user experience.
Accessibility
Physical controls are more accessible for users with visual impairments or limited dexterity. They can be operated by touch alone, even when wearing gloves or with wet hands, which is not possible with capacitive touch screens.
Reliability
Physical buttons tend to be more reliable in various environmental conditions and over the long term. They are less susceptible to software glitches and can provide a fail-safe option for critical functions.
Top 6 Trends in Hybrid Interfaces Shaping Automotive User Experience in 2024
Several trends are shaping the development of hybrid interfaces in the automotive industry:
Return of Physical Controls
Major automakers are reintroducing physical buttons for key functions. Volkswagen, for instance, has announced plans to bring back physical buttons on steering wheels in response to customer feedback. This move is part of a broader industry trend recognizing the value of tactile controls.
Smart Integration
Manufacturers are finding innovative ways to integrate physical controls with digital displays. For example, the Porsche Taycan features a curved display combined with physical buttons, creating a seamless blend of digital and analog controls.
Customizable Controls
Some automakers are experimenting with customizable physical controls that can be programmed to perform different functions based on user preferences. This approach combines the tactile benefits of physical buttons with the flexibility of digital interfaces.
Haptics in Cars
To bridge the gap between touch screens and physical buttons, many manufacturers are incorporating haptic feedback into their touch interfaces. This technology provides a tactile sensation when interacting with on-screen elements, mimicking the feel of physical buttons. By integrating haptic feedback in cars, automakers are enhancing the automotive user experience, making digital interactions more intuitive and providing drivers with a greater sense of control.
Integration of Voice Control in Cars
Voice control systems are becoming more sophisticated and are being integrated with hybrid interfaces to provide an additional layer of interaction. This allows drivers to control various functions without taking their hands off the wheel or eyes off the road. With the growing importance of voice control in cars, this technology is playing a key role in enhancing the automotive user experience by making interactions more intuitive and safer.
Augmented Reality (AR) in Cars
AR technologies are being incorporated into hybrid interfaces, projecting information onto the windshield or other surfaces. This allows for critical information to be displayed in the driver’s line of sight without relying solely on touch screen interactions. As AR in cars becomes more advanced, it is revolutionizing how drivers interact with their vehicles, enhancing navigation, safety alerts, and overall user experience in real-time.
Examples of Hybrid Interfaces in Modern Vehicles:
Volkswagen ID.2all Concept
Volkswagen’s ID.2all concept showcases an innovative approach to interior design, featuring a row of physical, backlit buttons below the touch screen for commonly used HVAC controls. It also includes a manual volume button and a large center knob for additional controls.
BMW iDrive System
BMW’s iDrive system combines a touch screen with a physical rotary controller, allowing users to interact with the infotainment system in multiple ways. This approach has been refined over several generations to balance digital flexibility with tactile control.
Mercedes-Benz User Experience (MBUX)
The MBUX system in newer Mercedes-Benz models combines a touch screen interface with physical trackpads on the steering wheel and center console, as well as voice control. This multi-modal approach allows drivers to choose their preferred method of interaction.
Mazda Connect
Mazda has resisted the trend towards large touch screens, instead opting for a smaller display controlled by a physical rotary knob and buttons. This approach prioritizes minimizing driver distraction while still providing access to modern infotainment features.
Some of the Latest Developments in Hybrid Interfaces Include:
- The integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and next-generation advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) along with increasing V2X infrastructure, moving the industry closer to autonomous driving functionality
- The rise of Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication technology, creating a safer, smarter, and more connected transportation ecosystem
- The development of more sophisticated in-vehicle infotainment (IVI) systems, offering improved performance, enhanced connectivity, and user-friendly interfaces
- The implementation of edge computing in vehicles, allowing for real-time data processing and analysis
- The adoption of Automotive Open System Architecture (AUTOSAR) to standardize and optimize connections between various applications and vehicles.
The evolution of hybrid interfaces in cars represents a significant shift in the automotive industry’s approach to automotive user experience and safety. By combining the flexibility of touch screens with tactile feedback and the reliability of physical controls, automakers are creating more intuitive, safer, and user-friendly interfaces. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in hybrid interfaces, including more sophisticated haptic feedback systems, improved voice control integration, and novel ways of blending physical and digital controls. The goal remains to create interfaces that enhance the driving experience while minimizing distractions and ensuring safety. The trend towards hybrid interfaces in cars demonstrates the automotive industry’s responsiveness to user needs and safety concerns. It also highlights the importance of balancing technological advancement with practical usability in the design of modern vehicles. As we move into an era of increasingly connected and autonomous vehicles, the role of well-designed hybrid interfaces will become even more crucial in shaping the future of automotive technology.