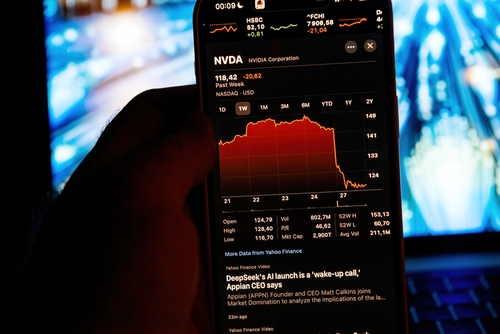
The meteoric rise of Chinese AI startup DeepSeek has sent shockwaves through Silicon Valley, exposing vulnerabilities in the West’s trillion-dollar AI investment strategy while offering a blueprint for democratizing artificial intelligence. By delivering high-performance models at a fraction of traditional costs, DeepSeek challenges the notion that AI dominance requires limitless capital—and its implications for global productivity are profound.
A Cost-Efficiency Earthquake
DeepSeek’s R1 model, developed for just $6 million, delivers performance comparable to OpenAI’s GPT-4 (which cost over $100 million to train). This unprecedented efficiency stems from three innovations:
- Open-Source Architecture: Unlike proprietary Western models, DeepSeek’s transparent framework allows global developers to refine and adapt its technology freely.
- Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) Design: Activates only 37B parameters per query vs. 1.7T in GPT-4, slashing computational demands.
- Hardware Agnosticism: Achieves results using restricted Nvidia H800 chips (post-US export bans) rather than premium H100s.
The financial fallout was immediate: $1 trillion vanished from US tech stocks in a single day, with Nvidia losing $600 billion as investors questioned the need for expensive GPUs.
Productivity Implications: Democratizing AI
DeepSeek’s model disrupts two critical barriers to AI adoption:
Cost
| Metric | DeepSeek R1 | GPT-4 |
| Training Cost | $6M | $100M+ |
| Energy/Query | 90% Less | Baseline |
| Business Pricing | 95% Cheaper | Market Rate |
Data compiled fromthis affordability enables SMEs and governments to deploy AI solutions without relying on Big Tech’s paywalls.
Accessibility
- Runs on energy-efficient devices (vs. cloud-dependent models)
- Excels in math/reasoning tasks critical for finance and engineering
- Supports multi-language applications out-of-the-box
Geopolitical Reckoning for Silicon Valley
The startup’s success undermines three Western assumptions:
- Capital = Dominance: Meta’s planned $65B AI spend now appears wasteful vs. DeepSeek’s lean approach.
- Hardware Superiority: By optimizing for restricted chips, China sidesteps US export controls.
- Innovation Monopoly: China files 2x more STEM PhDs and patents than the US.
As DeepSeek’s app topped US download charts, OpenAI’s Sam Altman admitted: “It’s legit invigorating competition,” while Trump called it a “Sputnik moment.”
The Productivity Horizon
Four sectors stand to gain most:
1. Healthcare
- Low-cost diagnostic tools for rural clinics
- Customizable models for rare disease analysis
2. Manufacturing
- Predictive maintenance AI deployable on factory-floor devices
- Supply chain optimization without cloud dependency
3. Government Services
- Affordable administrative automation (e.g., visa processing, tax filing)
- Real-time policy impact modeling
4. Education
- Localized tutoring bots running on school tablets
- Plagiarism detection avoiding Big Tech fees
However, risks persist. More often than not Benchmark performance ≠ real-world reliability, while data privacy concerns linger given China’s oversight laws.
Silicon Valley’s Crossroads
To compete, Western firms must:
- Embrace Open-Source Collaboration: As DeepSeek’s community-driven model spurs innovation
- Rethink Hardware Reliance: Invest in algorithmic efficiency over brute-force computing
- Pivot to Specialization: While DeepSeek targets broad usability, opportunities exist in niche domains like quantum AI
US tech giants are deploying a multi-pronged strategy to counter DeepSeek’s disruptive AI advances, combining technical innovation, political lobbying, and operational overhauls. Here’s how key players are responding:
1. Technical Countermeasures
- OpenAI accelerated its release schedule, pledging to deliver “better models faster” after DeepSeek-R1 outperformed GPT-4 on some benchmarks. CEO Sam Altman called the competition “invigorating” while privately pushing engineers to optimize training costs.
- Meta established “war rooms” where engineers reverse-engineer DeepSeek’s open-source code to replicate its efficiency gains. Their focus: adapting the Chinese model’s mixture-of-experts architecture to reduce computational demands by 40%.
- Nvidia is developing China-specific chips (H20 series) that comply with export controls while maintaining performance parity with restricted H100 GPUs.
2. Political & Regulatory Moves
- Lobbying for stricter IP protections, with OpenAI collaborating with the Commerce Department to prevent “knowledge distillation” of its models. Proposed measures include:
- Banning US agencies from using DeepSeek (already implemented by Navy/Congress)
- Pressuring app stores to remove DeepSeek’s software
- Investigating potential chip regulation violations
- Trump administration considering new export controls targeting:
- Cloud services that could host DeepSeek’s infrastructure
- Foundry partners producing advanced chips for Chinese firms
3. Cost Optimization Push
| Company | Cost-Cutting Measure | Target Savings |
| Microsoft | Shifting 30% AI workloads to lower-cost AMD GPUs | $4B/year |
| Developing “Chiplet” designs to reduce Nvidia dependency | 50% hardware costs | |
| Meta | Implementing DeepSeek-inspired sparse training techniques | 60% energy reduction |
4. Talent & Research Shifts
- Recruitment: Poaching Chinese AI researchers from DeepSeek’s 140-member team, offering 3x salaries
- Academic Partnerships: Stanford/Berkeley launching “Efficient AI” research centers funded by $200M tech consortium
- Open-Source Gambit: Meta plans to release Llama 3 under more restrictive licensing to prevent model distillation
5. Market Positioning
- Price Wars: Slashing API costs to match DeepSeek’s pricing:
- OpenAI reduced GPT-4 token costs by 75%
- Anthropic cut Claude 3 rates to $2.50/million tokens
- Vertical Integration: Tesla and Apple acquiring chip startups (Groq, Graphcore) to reduce reliance on Nvidia
While these strategies aim to neutralize DeepSeek’s threat, CFR analyst Paul Triolo notes: “The genie’s out of the bottle – efficiency-driven AI development is now table stakes”. With DeepSeek’s app still topping US download charts, the pressure remains on Silicon Valley to deliver both innovation and affordability.
The path forward was summarized by Yardeni Research: “Will DeepSeek sink the Magnificent Seven? Or teach them to swim smarter?” DeepSeek’s disruption ultimately signals AI’s maturation from a capital-intensive arms race to a productivity multiplier accessible to all. While US tech giants scramble to adapt, the real winners may be global consumers and businesses finally empowered to harness AI’s potential—without the premium price tag. As The Economist notes, this could be the catalyst for “an AI productivity boom that actually benefits Main Street over Wall Street.” The race is not over, but the rules have irrevocably changed.