This five‑part series is designed as a practical field guide for CXOs, CMOs, CDOs and digital leaders who know their martech stack is under‑leveraged but are unsure where to start fixing it. Across the series, the articles move from strategy to architecture, then into ROI, platform choices and execution, so leadership teams can see the whole chessboard rather than isolated tools or features. For Indian organisations navigating agentic AI, evolving data regulations and an increasingly complex vendor landscape, the series offers a structured way to understand what truly matters, what can wait, and how to turn martech from a cost line into an intelligent growth system.
Designing A 2026 Martech Architecture: Where Do AI Agents Actually Live?
The previous blog (From Martech Stack To Intelligent Growth System: Why 2026 Is A Breakout Year) established why martech must now function as an intelligent growth system. This blog turns that strategic lens into architecture: how should enterprise leaders think about Salesforce, Adobe, CleverTap, MoEngage, Netcore, LeadSquared, Zoho CRM, and emerging AI agents as an integrated ecosystem in 2026?
From Stacks To Systems: A 2026 Reference Architecture
Traditional diagrams of the martech stack are linear and tool‑centric. A 2026 architecture is better understood as three interconnected system layers—with a new, explicit layer for agents.
- Systems of record and engagement
These platforms store core entities (customers, accounts, transactions) and execute day‑to‑day interactions.- CRM and sales/service clouds: Salesforce, Zoho, LeadSquared.
- Enterprise marketing suites: Salesforce Marketing Cloud, Adobe Experience Cloud.
- Specialist engagement engines: CleverTap and MoEngage for behavioural engagement; Netcore for high‑volume, regulated messaging.
- Systems of insight and coordination
These unify data, derive intelligence, and allow designers and data teams to understand what is happening.- CDPs and RT‑CDPs: Salesforce Data Cloud, Adobe Real-Time CDP, and India‑centric CDPs such as FirstHive.
- Analytics and experimentation: BI tools, attribution platforms, experimentation frameworks.
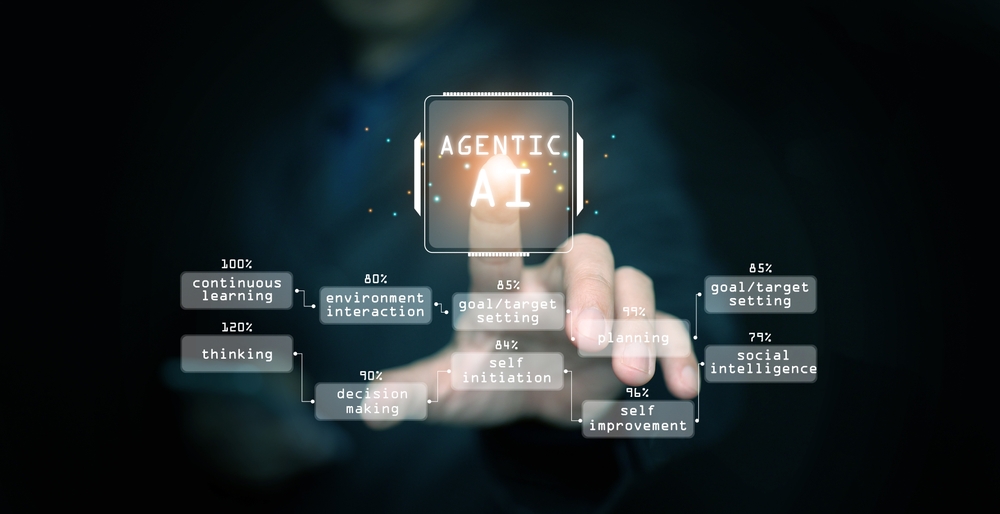
- System of autonomy (agent layer)
This is the emerging layer where agentic AI lives—reading from systems of insight and record, acting primarily through systems of engagement.- Native agent platforms: Salesforce Einstein + Agentforce, Adobe AI assistants.
- Cross‑stack agents: custom agents built on LLMs and orchestration frameworks, using protocols and APIs to safely perform tasks across tools.
The critical architectural challenge is not just integrating data flows, but defining how and where agents will operate: what they can see, where they can act, and how their actions are governed.
“The hardest question in 2026 is not ‘Which tool?’ but ‘Where will our agents live and what can they safely touch?’.”
Repositioning The Seven Platforms In An Agent-Ready World
- CleverTap – behavioural intelligence for high-frequency engagement
Primary role: deep behavioural system of engagement for app‑first businesses.
Agentic opportunity: agents can use CleverTap’s granular events to autonomously optimise onboarding, nudge sequences, and retention campaigns for millions of MAUs. - MoEngage – omnichannel orchestration and consent management
Primary role: omnichannel journey engine with strong consent and preference orchestration.
Agentic opportunity: agents can decide individual‑level channel mix and send times across email, SMS, WhatsApp, and push, while MoEngage enforces consent and regulatory rules. - Netcore Cloud – infrastructure backbone for transactional and regulated comms
Primary role: high‑reliability messaging infra and compliance automation for BFSI, fintech, and high‑volume senders.
Agentic opportunity: agents responsible for transactional and service workflows can rely on Netcore to ensure OTPs, alerts, and statements are delivered with audit trails and at scale. - LeadSquared – sales process acceleration for distributed teams
Primary role: specialised CRM for high‑volume lead management and field force coordination.
Agentic opportunity: agents can watch lead scores and SLA timers, automatically reassigning leads, triggering coaching alerts, or prioritising call lists for agents. - Zoho CRM (with Zia) – AI‑native localised CRM
Primary role: generalist CRM with strong India localisation and embedded AI assistant (Zia).
Agentic opportunity: Zia and external agents together can manage scoring, forecasting, and communication suggestions; a cross‑stack agent can extend these capabilities into other tools. - Salesforce – enterprise Customer 360 with Agentforce
Primary role: global standard for enterprise CRM, with integrated Sales, Service, Marketing, and Data Cloud.
Recent evolution: newer releases deepen Einstein Copilot and introduce Agentforce, enabling AI agents to execute workflows across Salesforce clouds.
Agentic opportunity: Salesforce can be the “home” for enterprise agents, which orchestrate sales, service, and marketing tasks with strong governance controls and trusted URL enforcement. - Adobe Experience Cloud – content-centric CX with RT‑CDP
Primary role: integrated ecosystem for content management, B2B marketing (Marketo Engage), and real-time orchestration (Journey Optimizer) on top of RT‑CDP.
Recent evolution: RT‑CDP Collaboration and new releases emphasise data collaboration, unified B2C/B2B strategies, and real‑time activation across brands.
Agentic opportunity: agents can operate on a rich canvas of content, journeys, and unified profiles to manage multi‑brand experiences across regions.
“Your architecture should make the division of labour between humans and agents explicit.”
India Architecture Patterns
- The “WhatsApp spine” pattern
For many Indian fintech and NBFC players, WhatsApp plus SMS has effectively become the communication spine: OTPs, KYC reminders, repayment nudges, and service queries all run through these pipes. In this pattern, Netcore or an equivalent infra provider anchors reliable messaging, MoEngage or CleverTap orchestrates context‑aware journeys, and Salesforce or a local CRM keeps the system of record. The agent layer sits on top, deciding which message to send, through which channel, at what risk level. - The “CDP‑first retailer” pattern
A fast‑growing Indian fashion retailer operating across metros and Tier‑2 cities implemented a CDP as the “brain” between POS, e‑commerce, and app data. Adobe Experience Cloud or Salesforce Data Cloud–style architectures enable unified profiles, which agents then use to personalise offers by store cluster, language, and basket behaviour.
“For Indian Fintechs, WhatsApp and SMS have become the communication spine; martech has to wrap around that reality.”
For CXOs, the architectural message is clear: don’t bolt agents onto yesterday’s stack. Design a martech architecture where systems of record, insight, and autonomy are explicitly defined and strategically aligned.